Self Portrait with a Beret, 1886 by Claude Monet. Source: Wikimedia Commons
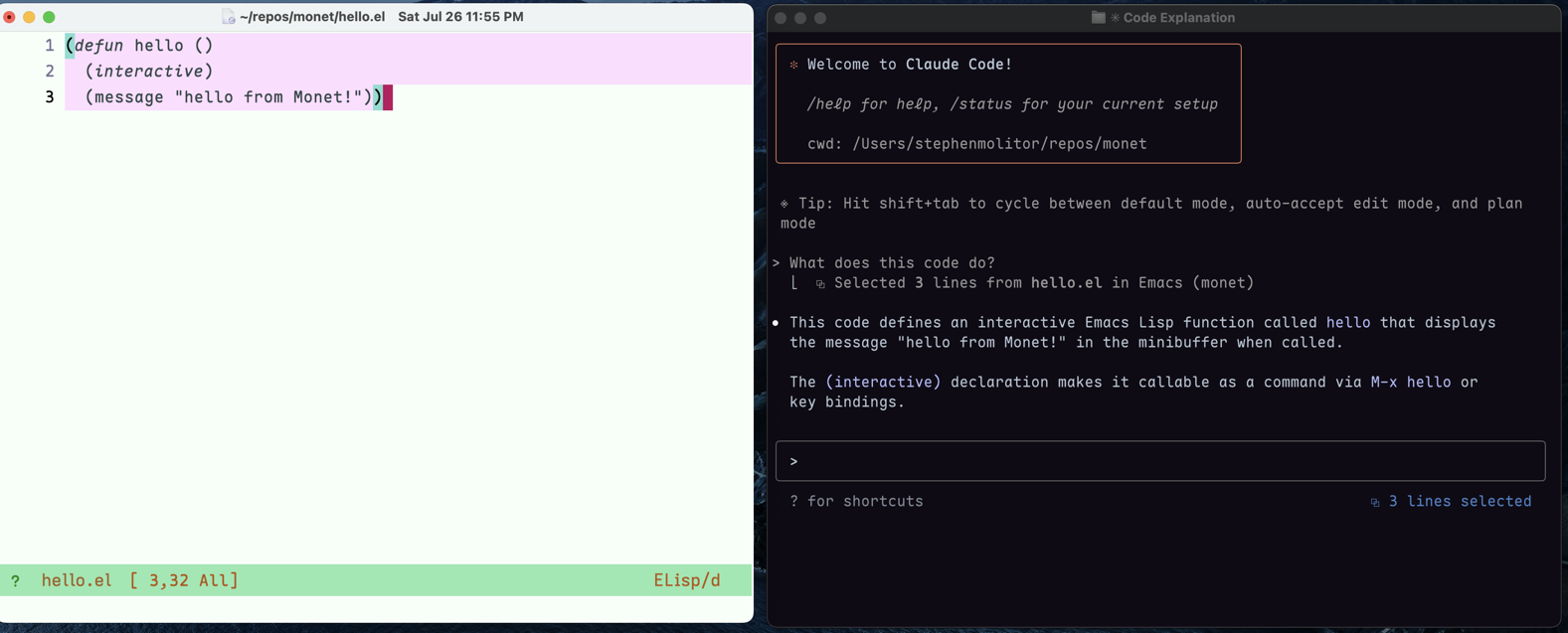
Monet is an Emacs package that implements the (undocumented) Claude Code IDE protocol, enabling Claude to interact with your Emacs environment through a WebSocket connection.
You can use Monet with Claude Code running in your favorite terminal emulator (Ghostty, Kitty, iTerm2, WezTerm), or with packages like claude-code.el that run Claude Code directly inside Emacs.
- Selection context: current selection in Emacs is automatically shared with Claude Code
- Send diagnostics from Flymake/Flycheck (and thus LSP in LSP modes) to Claude
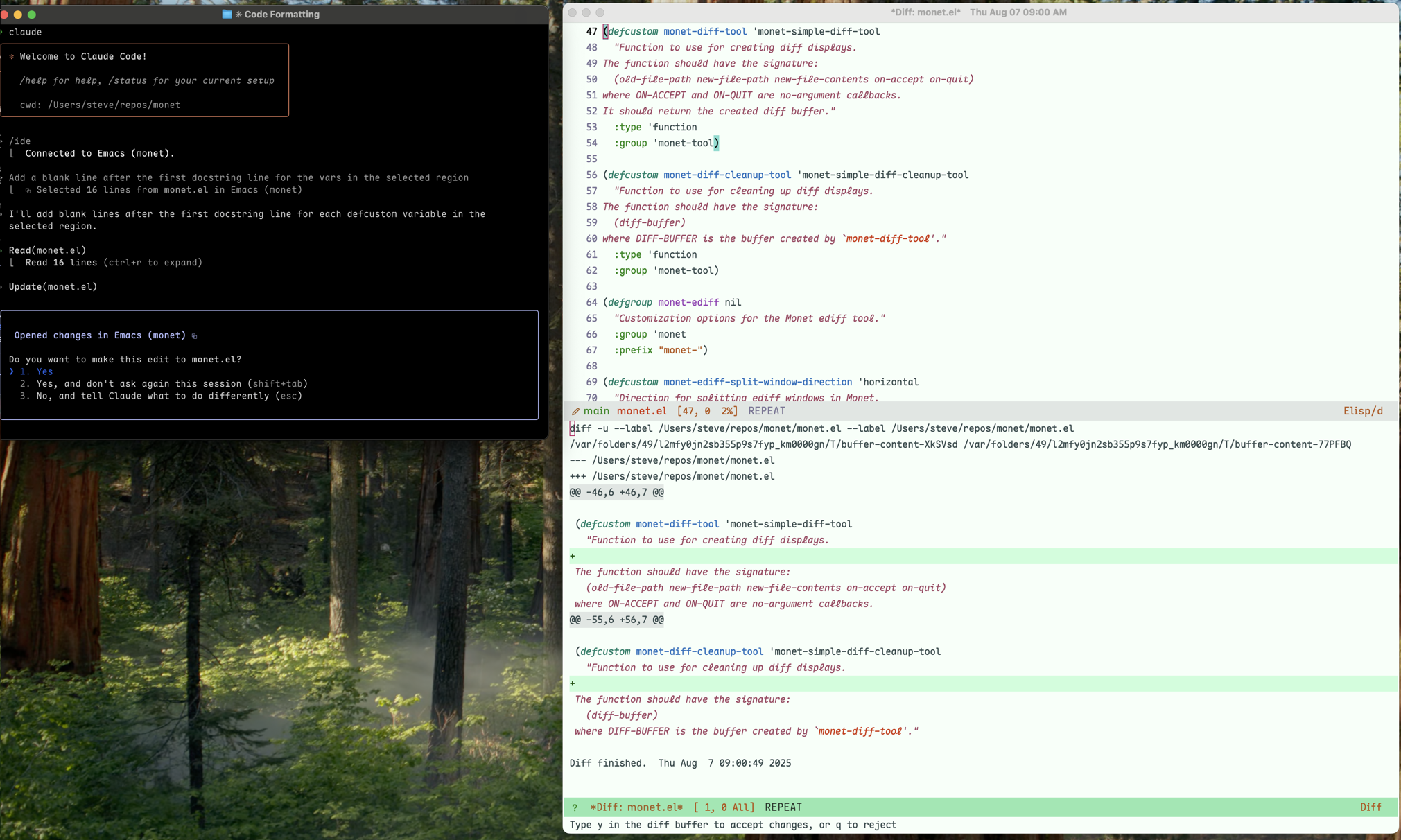
- Create diff views in Emacs before Claude applies changes
- Project-aware session management
- Multiple concurrent sessions support
- Emacs 30.0 or later
- websocket package
(use-package monet
:vc (:url "https://github.com/stevemolitor/monet" :rev :newest))(straight-use-package
'(monet :type git :host github :repo "stevemolitor/monet"))-
Clone this repository:
git clone https://github.com/stevemolitor/monet.git
-
Add to your Emacs configuration:
(add-to-list 'load-path "/path/to/monet") (require 'monet)
-
Enable Monet mode:
M-x monet-mode
-
Start a Monet server:
C-c m s ; Start server in current project/directory -
In Claude Code, start a new chat and use the /ide slash command to connect to your Emacs session.
To have Claude automatically connect to your Monet session set ENABLE_IDE_IDE=t before starting Claude.
If you have multiple Monet sessions for the same project you can do this to have Claude automatically connect to the desired instance:
ENABLE_IDE_INTEGRATION=t && CLAUDE_CODE_SSE_PORT=123456 && claudeMonet prints a message with the port number when you call monet-start-server (C-c m s). You can see the list of all running servers with their ports and directories via monet-list-sessions (C-c m l).
Using Monet with claude-code.el
You can use Monet with claude-code.el by adding this hook:
(add-hook 'claude-code-process-environment-functions #'monet-start-server-function)When claude-code.el starts a new session it will start and associate a Monet session with the current claude-code.el instance.
Sessions are automatically cleaned up (killed) when you exit the associated Claude session. When you exit Emacs all sessions are cleaned up. You can stop a session manually via monet-stop-server (C-c q).
Here's Monet in action - Claude running in Ghostty terminal communicating with Emacs:
When monet-mode is enabled, the following key bindings are available (default prefix: C-c m):
C-c m s- Start serverC-c m q- Stop server (with completion)C-c m Q- Stop all serversC-c m l- List active sessionsC-c m L- Enable loggingC-c m D- Disable logging
When Claude proposes code changes, Monet displays them in a diff view:
-
Simple Diff Tool (default): A read-only diff view showing the proposed changes
- Press
yto accept Claude's changes exactly as shown - Press
qto reject the changes
- Press
-
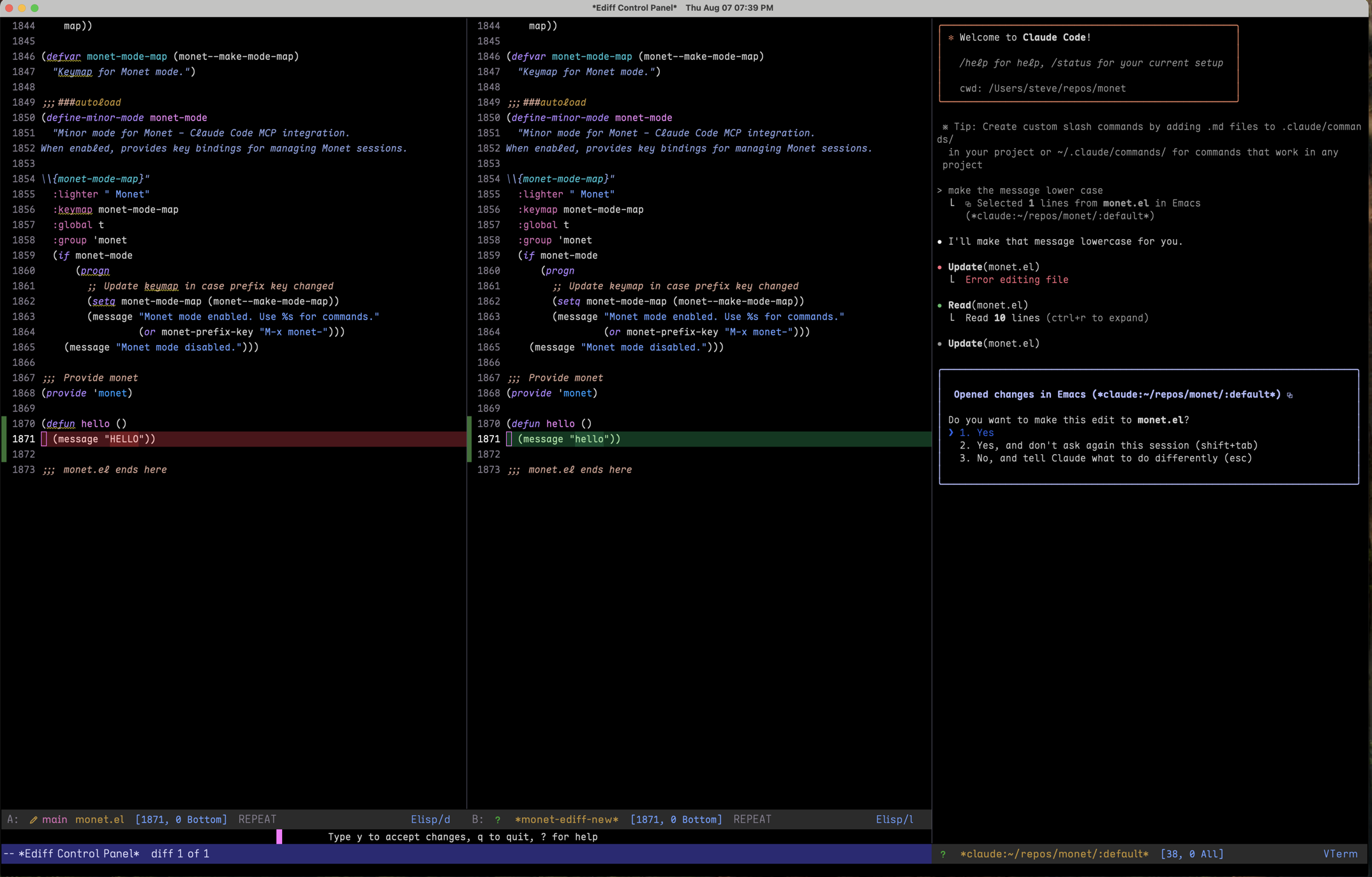
Ediff Tool: An interactive diff view that allows you to edit the changes before accepting
- Navigate between differences using
n(next) andp(previous) - Edit the proposed changes directly in the buffer
- Press
C-c C-cto accept your edited version (your changes will be sent to Claude) - Press
qto reject all changes
- Navigate between differences using
Important: With the ediff tool, any manual edits you make to the proposed changes are captured and sent to Claude when you accept. This allows you to refine Claude's suggestions before applying them.
Monet automatically creates session keys based on your context:
- When in a project (via
project.el), uses the project name - Otherwise, uses the current directory name
- Automatically generates unique keys for multiple sessions (e.g.,
project<2>)
With a prefix argument (C-u C-c m s), you can manually select a directory.
You can start multiple sessions per project, or have multiple
;; Change the prefix key (default: "C-c m")
(setq monet-prefix-key "C-c C-m")
;; Or disable prefix key and use M-x commands only
(setq monet-prefix-key nil)
;; Change log buffer name
(setq monet-log-buffer-name "*My Monet Log*")
;; Customize diff keybindings
(setq monet-ediff-accept-key "C-c C-a") ; Default: "C-c C-c"
(setq monet-ediff-quit-key "C-g") ; Default: "q"
(setq monet-simple-diff-accept-key "C-c C-c") ; Default: "y"
(setq monet-simple-diff-quit-key "C-g") ; Default: "q"
;; Change ediff window split direction
(setq monet-ediff-split-window-direction 'vertical) ; Default: 'horizontalMost MCP tools that Claude uses to interact with Emacs are now customizable. You can replace the default implementations with your own functions:
;; Custom file opener that confirms before opening
(defun my-open-file-tool (uri)
(when (y-or-n-p (format "Open %s? " uri))
(monet-default-open-file-tool uri)))
(setq monet-open-file-tool 'my-open-file-tool)
;; Custom diagnostics that only reports errors
(defun my-diagnostics-tool (&optional uri)
(let ((result (monet-flymake-flycheck-diagnostics-tool uri)))
;; Filter to only errors...
result))
(setq monet-diagnostics-tool 'my-diagnostics-tool)Available customizable tools:
monet-get-current-selection-tool- Get current text selectionmonet-get-latest-selection-tool- Get latest selection from any filemonet-open-file-tool- Open files in the editormonet-save-document-tool- Save documents to diskmonet-check-document-dirty-tool- Check for unsaved changesmonet-get-open-editors-tool- List open filesmonet-get-workspace-folders-tool- List project directoriesmonet-diagnostics-tool- Get diagnostics (defaults to Flymake/Flycheck)
Important: to customize the diff tool to use ediff, you must set both the diff tool and the diff cleanup tool:
(setq monet-diff-tool #'monet-ediff-tool)
(setq monet-diff-cleanup-tool #'monet-ediff-cleanup-tool)You can customize how Monet displays diffs by providing your own diff tool functions:
;; Use a custom diff tool
(setq monet-diff-tool 'my-diff-tool)
(setq monet-diff-cleanup-tool 'my-diff-cleanup)The diff tool function should take: (old-file-path new-file-path new-file-contents on-accept on-quit) and return a context object. The cleanup function takes that context object for cleanup.
To disable Monet's diff functionality entirely and use Claude's built-in diff display instead:
(setq monet-diff-tool nil)When disabled, Claude will show proposed changes in its native interface rather than creating diff views in Emacs.
Monet creates a WebSocket server that Claude Code connects to via MCP. This allows Claude to:
- Browse and open files in your project
- See real-time diagnostics from your linters
- Create side-by-side diffs for code review
- Track your current selection/cursor position
Each session is isolated to a specific directory/project, ensuring Claude only accesses files within the intended scope.
- Check active sessions:
C-c m lto list all running servers - Enable logging:
C-c m Lto see all MCP communication