What Is 404 Not Found and How To Fix It

A 404 Not Found error is one of the most common and frustrating experiences users encounter online. It signals that a requested web page is missing, leaving visitors stranded and potentially damaging your site’s credibility. For website owners, 404 errors are more than just a nuisance—they can harm user experience, disrupt SEO efforts, and cost valuable traffic.
In this post, we’ll break down what 404 Not Found means, why it happens, and, most importantly, how to fix it to keep your website running smoothly and effectively.
What is a 404 error?
A 404 error occurs when a web server cannot find the page requested by the user. This typically happens because the URL is incorrect, the page has been deleted, or the resource has moved without updating the link. It is an HTTP status code indicating “Not Found.”
When a page is removed or relocated without a proper redirect, both users and search engines encounter a 404 error, signaling that the page no longer exists. While this error is common, it can frustrate users seeking information. Excessive 404 errors can also give search engines the impression that a site is poorly maintained, potentially harming SEO performance.
What does a 404 error look like?
A 404 error can appear differently depending on whether you’re the end user or the site administrator. Each perspective offers valuable clues for diagnosing and resolving the issue.
On the user’s end
A 404 error can appear differently depending on whether you’re the end user or the site administrator. Each perspective offers valuable clues for diagnosing and resolving the issue.
On the User’s End
When users encounter a 404 error, their browser typically displays messages such as ‘404 Error,’ ‘Page Not Found,’ or ‘The requested URL could not be found.’ This usually indicates one of three issues:
- The page was moved without a proper redirect (typically a 301 redirect)
- The page no longer exists
- The URL was mistyped
The exact appearance of a 404 error depends on the website’s custom 404 page design. Some sites simply display a text message, while others provide helpful links to guide users to other areas of the site.
Users may also encounter ‘soft 404s,’ where a page shows a ‘not found’ message but still returns an HTTP 200 (OK) status. Soft 404s can confuse users and mislead search engines into thinking the page is available, potentially causing indexing issues. Clear error communication improves user navigation and ensures search engines handle the site correctly.
On the server’s end
From the server’s perspective, a 404 error indicates that the requested URL could not be found and has been recorded as an HTTP 404 error in the server logs. This issue can arise for various reasons, such as:
- A misspelled URL
- A page that was moved or deleted
- A more specific issue, such as a 404.1 (Site Not Found) or 404.3 (MIME Type Restriction), which provide additional diagnostic details
Server logs are invaluable for webmasters in identifying and resolving 404 errors. By analyzing logs, administrators can:
- Determine how frequently 404 errors occur
- Identify patterns, such as broken internal links or outdated external links leading to nonexistent pages
Resolving these issues is a core aspect of technical SEO and on-page SEO best practices. Properly addressing 404 errors ensures a better user experience and helps maintain search engine trust in the site.
Hard 404 vs. soft 404
Understanding the difference between hard and soft 404 errors is essential for diagnosing issues and resolving problems before they negatively impact users or search engines.
Hard 404 errors
A hard 404 error occurs when a server returns a proper HTTP 404 status code, signaling that the requested content is missing. These errors accurately reflect the state of your site and communicate clearly to both users and search engines that the page no longer exists.
Search engines typically de-index pages that return a hard 404 status, ensuring the site’s index remains clean and accurate. This helps prevent users from landing on non-existent pages and improves the overall integrity of your site in the eyes of search engines.
Soft 404 errors
A soft 404 error occurs when a server returns an HTTP 200 (OK) status code, but the page displayed to users is a “not found” message or similar placeholder content. This creates the illusion that the page exists, even though it does not.
Soft 404s can confuse search engines, causing them to index pages that lack meaningful content, which negatively impacts how your site is ranked and indexed.
Soft 404 errors are often caused by:
- Poorly configured custom error pages
- Improperly written scripts that fail to return the correct HTTP status code
Why fixing soft 404s matters
Addressing soft 404s by properly serving hard 404 errors is critical for maintaining your site’s integrity. Hard 404s:
- Clearly communicate to search engines that a page is missing, preventing unnecessary indexing
- Signal professionalism and attention to detail in the eyes of users and search engines alike
Fixing soft 404s ensures your site is accurately represented in search engine indexes, improving both user experience and SEO performance.
How to craft a helpful and user-friendly 404 page
It’s highly recommended to spend time designing a 404 page. Why does the design of a 404 error page matter? A well-designed 404 page can help users stay on your site despite encountering a missing page, turning a potentially frustrating moment into a positive experience. It’s also an opportunity to reinforce your brand and keep users engaged.
Here are key tips and guidelines for creating a user-friendly and effective 404 page:
1. Keep it simple and clear
Your 404 page should communicate clearly that the requested page can’t be found. Use straightforward language like, ‘Oops! The page you’re looking for isn’t here,’ to make it easy for users to understand what happened. Avoid technical jargon, and instead focus on clarity and simplicity to help users quickly grasp the issue and move on.
2. Include a search bar
A search bar is one of the most effective tools to help users stay on your site. By offering a way to search for similar or related content, you give users a chance to find what they’re looking for without leaving. Place the search box in a prominent location and ensure it delivers relevant results to improve the user experience.
3. Provide helpful links
Directing users to other parts of your site can keep them engaged even if the page they were looking for is unavailable. Include links to high-value areas like your homepage, contact page, or special offers. You might also feature links to your blog, FAQs, or recently published content to encourage users to explore further.
4. Use visual appeal
Incorporate your brand’s colors, style, and design elements into the 404 page to keep it visually appealing. Adding creative graphics or a touch of humor can turn a potentially negative experience into a memorable one. Done well, this approach can even enhance user loyalty and leave a positive impression of your brand.
5. Offer user support
Providing a way for users to report broken links or seek assistance can add value to your 404 page. Include a support link or email address so users can contact you if needed. This demonstrates that you care about their experience and allows you to address issues before they impact your site’s overall health.
6. Clear navigation
Make it easy for users to return to functional areas of your site. Include links to your homepage, major categories, or a sitemap. Clear website navigation ensures users can continue exploring your content without frustration, reducing the likelihood of them leaving your site altogether.
How does a 404 error affect your SEO?
404 errors can significantly impact your site’s health, user experience, and, ultimately your search rankings. Let’s examine how these errors influence your SEO performance and explore solutions for keeping your site healthy.
1. Poor user experience
When users encounter a 404 error page, it often leads to frustration. This negative experience can result in higher bounce rates and lower user engagement metrics, both of which harm your chances of ranking on the first page of search results.
Search engines, including Google, monitor user behavior closely. If they detect that users frequently leave your site after landing on a 404 page, they may interpret this as a sign of low-quality content and lower your organic rankings accordingly.
2. Difficulty ranking pages
Excessive 404 errors can disrupt search engine crawling and indexing. When search engines encounter too many broken links, they may struggle to navigate your site effectively, reducing its visibility in search results.
Additionally, broken links waste valuable crawl budgets. Google’s web crawlers may spend unnecessary time attempting to resolve or repeatedly recrawl 404 errors, leaving less time to index other important pages on your site. Regular site audits with SEO tools can help identify and resolve these issues to maintain efficient indexing.
3. Reduced SERP visibility
Pages that return 404 errors are not indexed by search engines, which reduces the total number of pages from your site that can appear in search results. This, in turn, lowers your site’s visibility and authority in the eyes of search engines.
Frequent 404 errors can erode trust with search engines. If your site consistently serves broken pages, it signals unreliability, making it harder for your site to rank for targeted keywords. To maintain your SERP position and authority, it’s essential to minimize 404 errors.
How to find 404 errors
Identifying and resolving 404 errors is vital for maintaining a healthy and user-friendly website. Below are effective methods to locate and address these issues:
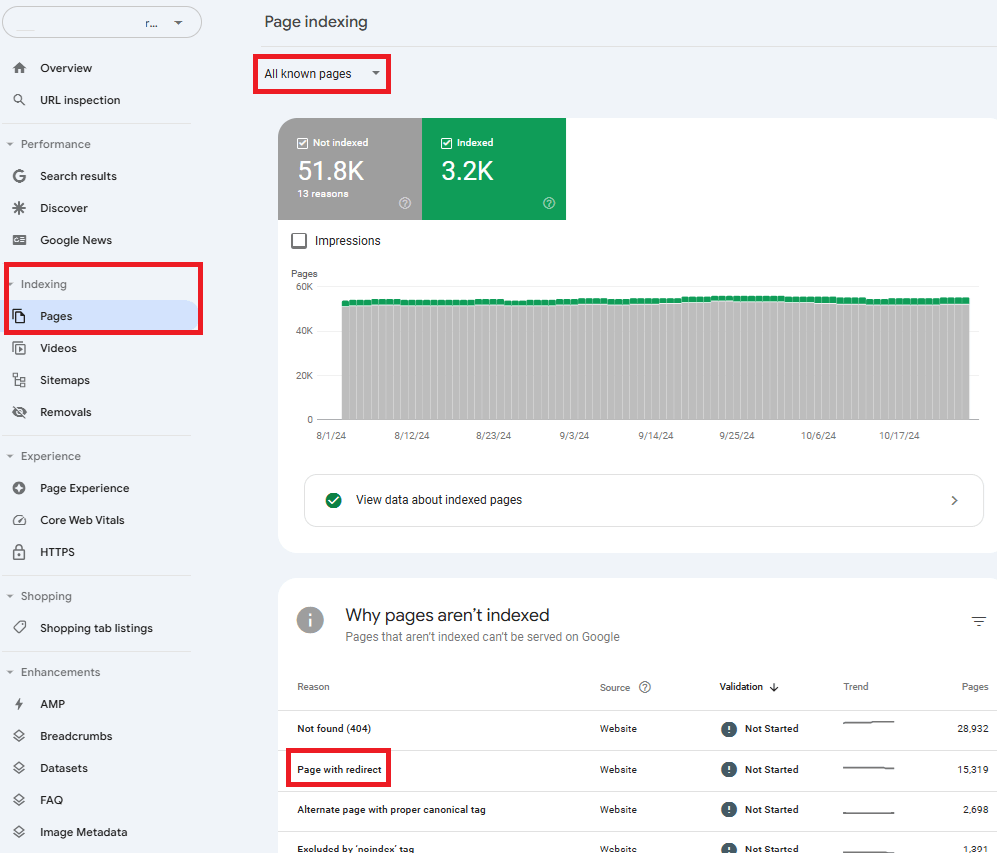
1. Google Search Console
Google Search Console is an invaluable tool for monitoring your site’s health. Navigate to Indexing > Pages to view URLs detected by Google’s crawlers. By default, the tool displays All Known Pages, but you can filter for All Submitted Pages to narrow your focus.
This tool provides detailed insights, including the frequency of 404 errors and the specific pages affected. Addressing these errors helps improve both your site’s SEO and user experience. However, it has limitations:
First, it only reveals pages Google has crawled, leaving other potential issues undetected. Second, it often includes duplicate URLs with parameters (e.g., domain.com/slug/?parameter), which can clutter your data and complicate analysis.
2. Google Analytics
Google Analytics allows you to measure 404 errors by analyzing user behavior and setting up custom reports or alerts. You can create a 404 alert that tracks pages with “404” in the title to identify broken links.
Additionally, analyzing user behavior flow helps determine how users arrive at error pages. This information enables you to correct broken links and reduce drop-offs, ultimately enhancing your site’s usability.
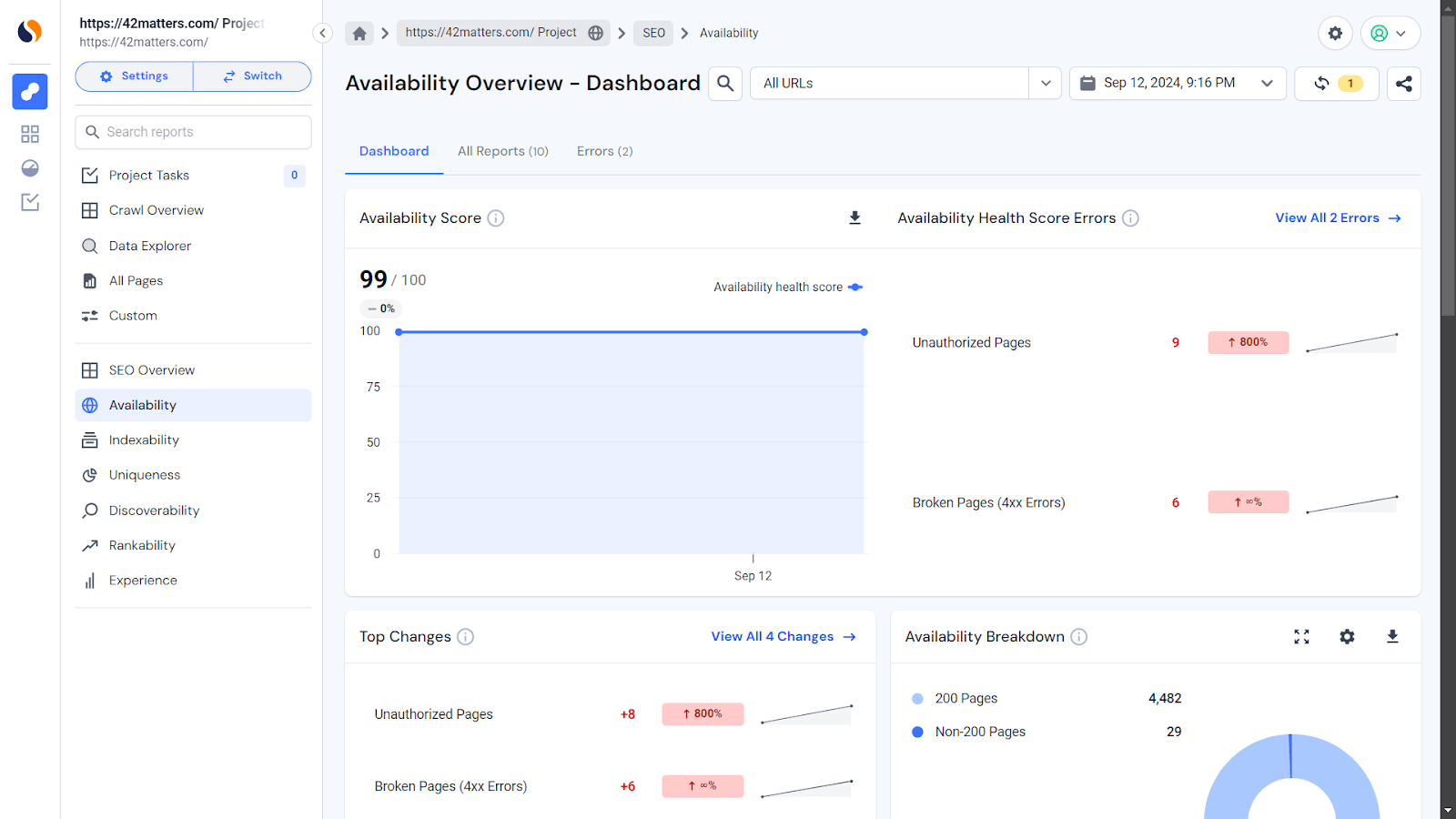
3. Similarweb Site Audit tool
The Similarweb Site Audit tool offers a broader view of your site’s health, including detecting and tracking broken pages (4xx errors). You can scan for 404 errors under SEO > Availability > Broken Pages (4XX) with a single click.
This tool is ideal for proactive maintenance. By running regular audits, you can monitor trends, address errors before they escalate, and receive actionable tips to improve overall site health.
How to fix a 404 error on your website
Once you’ve identified 404 errors on your site, addressing them promptly is crucial to maintaining both user experience and SEO performance. Here are three effective strategies to fix these errors and ensure your site remains fully functional:
1. Remove the broken URL
Determine whether the URL is still relevant or necessary. If it’s outdated or no longer serves a purpose, consider removing it entirely. However, ensure that its removal won’t negatively impact usability or incoming links.
Removing old or unused URLs simplifies your site’s structure, making it easier for search engines to crawl and index the remaining pages. Conducting regular content audits can help you identify URLs that are no longer relevant or fail to meet user needs, enabling you to streamline your site efficiently.
2. Fix the broken URL (status code 404 to status code 200)
If the 404 error is caused by a typo or a misplaced link, correcting the link resolves the issue. Tools like website crawlers or link checkers can help you identify and fix internal links pointing to nonexistent pages.
This approach ensures that the URL returns a 200 OK status code, which is essential for maintaining proper link equity flow. Regularly crawling your site helps catch errors early, supports your SEO efforts, and ensures a smooth user experience.
3. Redirect the broken URL (status code 404 to status code 301)
For pages that have been moved or repurposed, set up a 301 redirect to guide users and search engines to the correct location. A 301 redirect indicates that the page has been permanently moved, preserving link equity and user satisfaction.
By redirecting broken URLs, users and search engines are seamlessly directed to the updated page instead of encountering a 404 error. Properly configured redirects maintain your site’s authority and ensure valuable link equity flows to the right destination.
Monitor your site for 404s regularly
Regular monitoring of 404 errors is essential for maintaining a clean and functional website. Tools like Google Search Console, Google Analytics, and Similarweb’s Site Audit tool make it easier to identify and address these issues promptly, helping you avoid keyword losses and ensure a positive user experience.
Set up scheduled audits and automated reports in our audit tool to detect 404 errors as soon as they occur. This proactive approach helps you:
- Keep your website healthy
- Support users by reducing frustrating dead ends
- Protect and enhance your site’s SEO performance
Addressing 404 errors consistently is far more manageable than allowing problems to accumulate over weeks or months. Regular monitoring ensures your site stays optimized and delivers a seamless experience for both users and search engines.
Stay on top of 404 errors
Fixing and preventing 404 errors is critical to maintaining an optimal user experience and strong SEO performance. Use tools like Similarweb to identify any existing 404 errors and address them promptly.
By taking swift action to resolve these issues, you ensure that visitors and search engines encounter a seamless browsing experience. Don’t let 404 errors disrupt your site’s usability—start fixing them today to keep your website running smoothly and effectively.
FAQs
What is a 404 error?
A 404 error is an HTTP status code indicating that a requested web page cannot be found on the server. This typically occurs due to an incorrect URL, or because the page has been moved or deleted.
What causes 404 errors?
404 errors can result from several issues, including:
- A broken link.
- A typo in the URL.
- Accidental deletion of a page without updating the URL.
- Server misconfiguration.
In all cases, the server fails to locate the requested resource.
How often should I monitor for 404 errors?
Regular site audits are essential to catch and fix 404 errors. Use tools like Google Search Console, Google Analytics, and Similarweb’s Site Audit Tool to identify issues. Schedule these audits either monthly or quarterly, depending on your site’s traffic and the frequency of updates.
How do 404 errors affect SEO?
404 errors negatively impact both user experience and SEO. They can:
- Increase your site’s bounce rate as users leave after encountering broken pages.
- Lower your search engine rankings, as search engines interpret numerous broken links as poor site quality.
Fixing 404 errors helps maintain a strong online presence and ensures better performance in the SERPs.
Why should I always check for 404 errors?
Regular monitoring ensures your site runs smoothly for users and search engines. Catching and resolving these errors early prevents them from harming the user experience or your search engine rankings. Consistent maintenance is key to a healthy and efficient website.
Track Gen-AI And Organic KPI's On The #1 SEO Platform
Give it a try or talk to our marketing team - it’s free!