A Complete Guide to Ecommerce Faceted Navigation

Are your users struggling to find what they need? The harder it is for them to navigate your site, the more likely they are to leave and spend their hard-earned money with your competitors.
If your site’s structure is causing frustration, faceted navigation could be the solution.
In this post, we’ll explore what faceted navigation is, when it’s the right choice, and how to implement it effectively.
What is faceted navigation?
Faceted navigation is a website feature that helps online shoppers refine their search for products, making it easier to browse large catalogs. It allows users to apply multiple filters, such as size, color, brand, or price, to narrow down their options. This enhances navigation while aligning with customer expectations for a seamless experience.
However, faceted navigation can create SEO challenges, such as generating hundreds of redundant URLs. Proper management is essential to preserve SEO integrity and prevent issues like duplicate content or crawl budget wastage.
Faceted navigation and user experience
Faceted navigation enhances the user experience by enabling personalized searches, which can significantly increase conversion rates. By tailoring results to user preferences, it creates a more intuitive and enjoyable shopping journey.
However, this functionality must be carefully managed to prevent SEO mistakes, such as URL overload, which can harm search engine performance. When implemented with effective SEO techniques, faceted navigation can improve site interaction and searchability, making it easier for users to find what they need.
How does faceted navigation work
Faceted navigation allows users to browse large product inventories efficiently by applying filters such as price, brand, size, or other attributes. Each time a user applies a filter, the page dynamically updates to display matching items, and a unique URL is generated to reflect the selected options. This ensures a seamless experience, allowing users to revisit or share their personalized search results easily.
While user-friendly, faceted navigation can pose significant SEO challenges. Each dynamically generated URL can result in an overwhelming number of pages, leading to issues like crawl budget waste. Search engines may expend resources indexing low-value or duplicate pages, diverting attention from higher-priority content.
To address these challenges, businesses must implement effective SEO strategies:
- Canonical tags: Specify the primary page for search engines to prioritize, reducing duplicate content issues.
- Noindex directives: Prevent certain pages from appearing in search results, minimizing the risk of duplicate content impacting SEO performance.
- Robots.txt file: Block specific URLs from being crawled, ensuring search engines focus on core, high-value pages.
Effective management also requires aligning user experience with SEO strategies. A robust internal linking framework helps search engines navigate to important pages, while periodic audits of crawling behavior allow for adjustments to the robots.txt file and other SEO measures.
When implemented thoughtfully, faceted navigation can enhance usability without compromising search engine performance. This approach creates a balance, enabling e-commerce platforms to deliver an exceptional user experience while maintaining strong SEO integrity—a win-win for both users and search engines.
How to use faceted navigation to get more traffic
When implemented correctly, faceted navigation can generate significant traffic for your site. By strategically applying techniques such as incorporating long-tail keywords, ensuring proper page indexation, and optimizing URL structures, you can make your site more searchable and attract more visitors. Here’s how to leverage faceted navigation for better online visibility:
1. Identify long-tail keyword variations
Long-tail keywords are specific and reflect the intent of the user directly. To incorporate these keywords effectively into your faceted navigation, analyze your audience’s search patterns to discover relevant variations. By including long-tail keywords, you enhance your chances of ranking for a broader range of search queries, driving more qualified traffic to your site.
2. Make faceted navigation pages indexable
Proper indexing of faceted navigation pages is crucial for optimal SEO performance. Use robots.txt to block search engines from crawling insignificant filter combinations, and apply noindex tags to prevent duplicate content issues. Focus on indexing pages with substantial keyword potential to improve visibility in search rankings. This targeted approach enhances your site’s relevance by prioritizing pages that are most likely to attract meaningful traffic.
3. Optimize the URLs for search
URLs generated through faceted navigation should be clear, concise, and SEO-friendly. Avoid unnecessary clutter such as session IDs or extraneous parameters. Instead, create keyword-rich, hierarchical URLs that improve both user experience and search visibility. Use canonical tags to consolidate duplicate URLs and preserve link equity. Regular site audits are essential to maintain a well-organized URL structure, ensuring better site performance and search engine presence.
Faceted search best practices
Optimizing faceted navigation is critical to the success of your ecommerce website, as it directly impacts both user satisfaction and SEO. Achieving a balance between user-friendly design and technical efficiency is essential for effective faceted search functionality. Well-designed filters enhance navigation, reduce user confusion, and contribute to lower bounce rates while boosting conversions.
So, how do you implement faceted navigation effectively? Here are the key practices to achieve optimal performance:
1. Faceted pages indexing
Faceted page indexing involves selectively allowing search engines to index faceted pages, focusing on valuable content while avoiding duplication. By prioritizing pages rich with unique, high-quality content, you can maintain strong search engine visibility and attract meaningful traffic. Tools like URL parameters and canonical tags are integral to this approach, as they help reduce redundancy and maintain web efficiency by streamlining the indexing process.
a) Index high-demand, unique faceted pages
Focus on indexing faceted pages that are popular and provide unique, relevant content. These pages enhance search rankings by addressing specific user queries and delivering a better user experience. For example, a page titled ‘Blue Summer Dresses’ could attract significant seasonal interest during summer, driving traffic and boosting rankings. The key is to develop content that meets user needs while maximizing ROI, ensuring your site remains competitive and effective.
b) Use noindex, robots.txt, or canonicalization for low-demand pages
For pages with low demand or minimal value, implement noindex tags, robots.txt, or canonical tags to optimize web resources and conserve search engine crawl budgets. This deliberate strategy helps direct attention to more valuable pages, improving overall site efficiency. For instance, by excluding less relevant pages from indexing, you enable search engines to focus on content that aligns with user interests, enhancing the site’s performance and visibility.
2. Use AJAX and limit internal links
Incorporating AJAX into your website enhances dynamic product sorting, enabling faster loading and a smoother user experience without requiring page reloads. A well-planned internal link structure is equally important for improving user experience and search visibility. By reducing excessive internal links, you simplify website navigation, making it easier for users and search engines to access important content. This streamlined approach supports better search engine performance and usability.
3. Make URLs shareable
Faceted navigation URLs should be easy to share and include relevant parameters. Shareable URLs encourage social media engagement and help drive organic traffic. Thoughtfully organized, simple URLs not only enhance user experience but also improve your site’s outreach and visibility by making your content more presentable and accessible.
4. Ensure URLs are clean
A well-structured website relies on clean, consistent URLs. Streamlined URLs reduce crawl load for search engines and improve navigation for users. Regular updates to URLs, such as removing unnecessary parameters and ensuring relevance, keep them concise and functional. Filters can also be used effectively to tailor URLs, making them easier to share and shortening them as needed. This approach enhances SEO performance, making your content more accessible and contributing to a positive user experience.
Use parameters for non-content values to simplify URLs
Utilize URL parameters for elements that do not affect page content, such as session IDs or tracking codes, to maintain clean and simple URLs. Avoid cluttering URLs with unnecessary directories or paths. Proper parameterization ensures a well-organized and streamlined site structure, improving both user navigation and search engine indexing efficiency.
5. Provide alternate crawl paths to important pages
Establish clear, well-defined crawl paths to ensure search engine crawlers can easily access critical pages. Highlighting these pathways enables strategic prioritization of key content, boosting its ranking potential and enhancing the user experience. An orderly and intuitive site layout promotes efficient indexing and helps maintain the visibility and prominence of essential pages.
6. Use standard URL encoding with key-value pairs
Implement consistent URL encoding with key-value pairs to simplify crawling and improve website structure. This standardization enhances usability and search engine efficiency by creating a predictable and organized framework. A well-structured encoding system supports both SEO and user experience simultaneously.
7. Prevent unnecessary URL creation for user-generated values
Restrict the creation of URLs for user-generated data, such as geographic information, to maintain a clean and manageable URL structure. Avoiding excessive URL variations prevents system overload and ensures more effective indexing. A clear and controlled approach to user values aligns indexing practices with site objectives and preserves search engine efficiency.
8. Disable filtering options with zero results
Disable filters that yield no results to improve user experience and the shopping process. Focusing on pages with potential value will save you crawl resources and direct attention to meaningful content. This strategy not only improves SEO performance but also increases the chances of users interacting with relevant and useful content.
9. Add breadcrumbs
Breadcrumbs create a clear and structured path that shows users exactly where they are located on your site. Users can jump between categories and subcategories in a click. No need to retrace their steps manually. In addition, breadcrumbs reflect your URL hierarchy for a more predictable and user-friendly browsing experience.
And guess what? It also adds SEO bonus points! Search engines love breadcrumbs because it helps them understand your site’s organization.
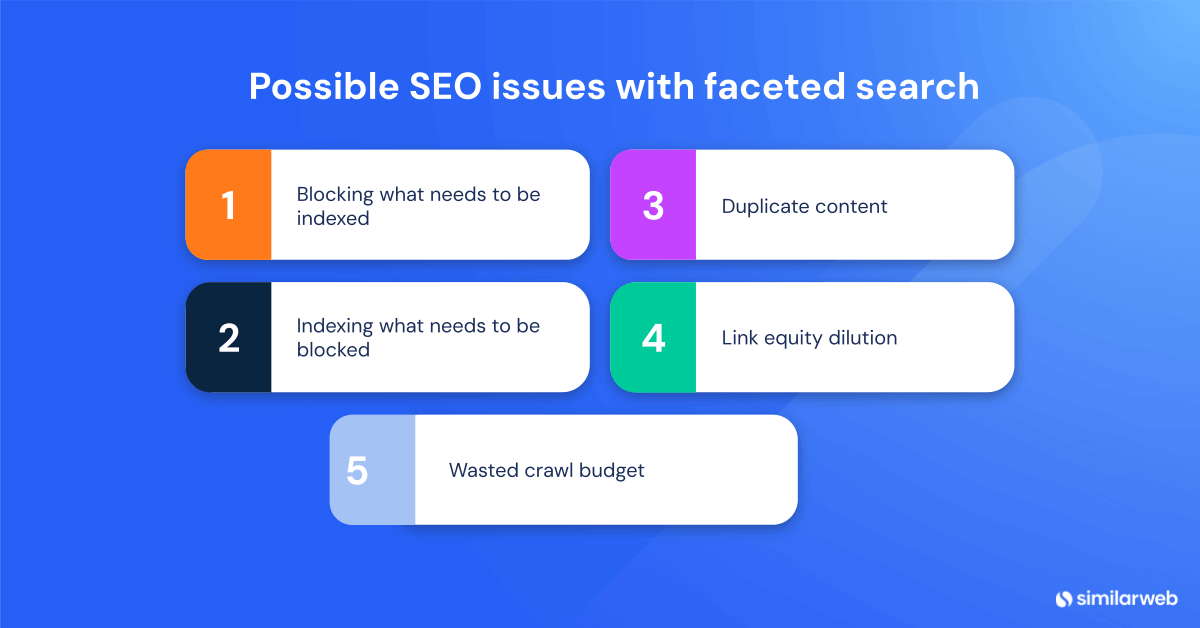
Possible SEO issues with faceted search
Faceted navigation is versatile but presents unique SEO challenges, particularly for e-commerce websites. Effective management is essential to avoid issues that can negatively impact site performance. Below are common obstacles and strategies to address them:
1. Blocking what needs to be indexed
Misconfigured robots.txt files or noindex tags can inadvertently block critical pages, reducing search engine visibility. Striking the right balance between blocking unnecessary pages and indexing essential ones ensures important information remains accessible and visible in search results. This balance is crucial for maintaining user engagement and search performance.
2. Indexing what needs to be blocked
Conversely, indexing minor or irrelevant pages diverts crawl resources from key content. Implement a strategic indexing approach that prioritizes core, high-value pages while excluding underperforming ones. This ensures efficient use of crawl budgets and highlights the most relevant content.
3. Duplicate content
Duplicate content across multiple URLs can dilute a page’s authority and confuse search engines. Using canonical tags effectively assigns a preferred version of a page, guiding search engines to the correct URL. This prevents overlap, maintains content relevance, and consolidates page authority.
4. Link equity dilution
Dispersed internal links can dilute link equity, reducing the ranking potential of important pages. Optimize your internal linking structure to concentrate link equity on high-priority pages. This improves their authority and increases the likelihood of favorable search rankings.
5. Wasted crawl budget
Irrelevant or redundant URLs generated by faceted navigation can consume crawl resources, diverting search engines from more significant pages. Proactive URL management and careful configuration of filters help focus search engine attention on valuable content. This approach ensures efficient indexing and improves clarity in search results.
Find faceted navigation issues
Addressing challenges related to faceted navigation requires identifying the underlying issues before implementing solutions. Ignoring these problems can harm your site’s performance and create hurdles for users searching for specific products. Begin by recognizing common issues such as index bloat and adopting effective content navigation strategies to resolve them. Utilizing specialized tools designed for performance analysis makes it significantly easier to identify and address these problems, ensuring a smoother user experience and improved site efficiency.
1. Site: command
The site: command is a quick and effective tool for identifying potential issues like index bloat. Simply type site: followed by your domain (e.g. site:yourdomain.com) in Google to see the number of URLs Google has indexed. If this number exceeds your target URL count, it’s a clear warning sign of index bloat. While this method doesn’t provide precise data, its speed and ease of use make it a practical starting point for spotting issues.
2. Google Search Console coverage report
The Google Search Console Coverage Report is invaluable for identifying crawling and indexing challenges. In the ‘Coverage’ section, the count of ‘Valid’ pages shows how many pages Google has indexed. A sudden increase in valid pages after implementing faceted navigation may indicate index bloat. Additionally, using XML sitemaps can help pinpoint sections of your website that might be unnecessarily indexed due to misconfigured filtering systems.
3. Similarweb Site Audit tool
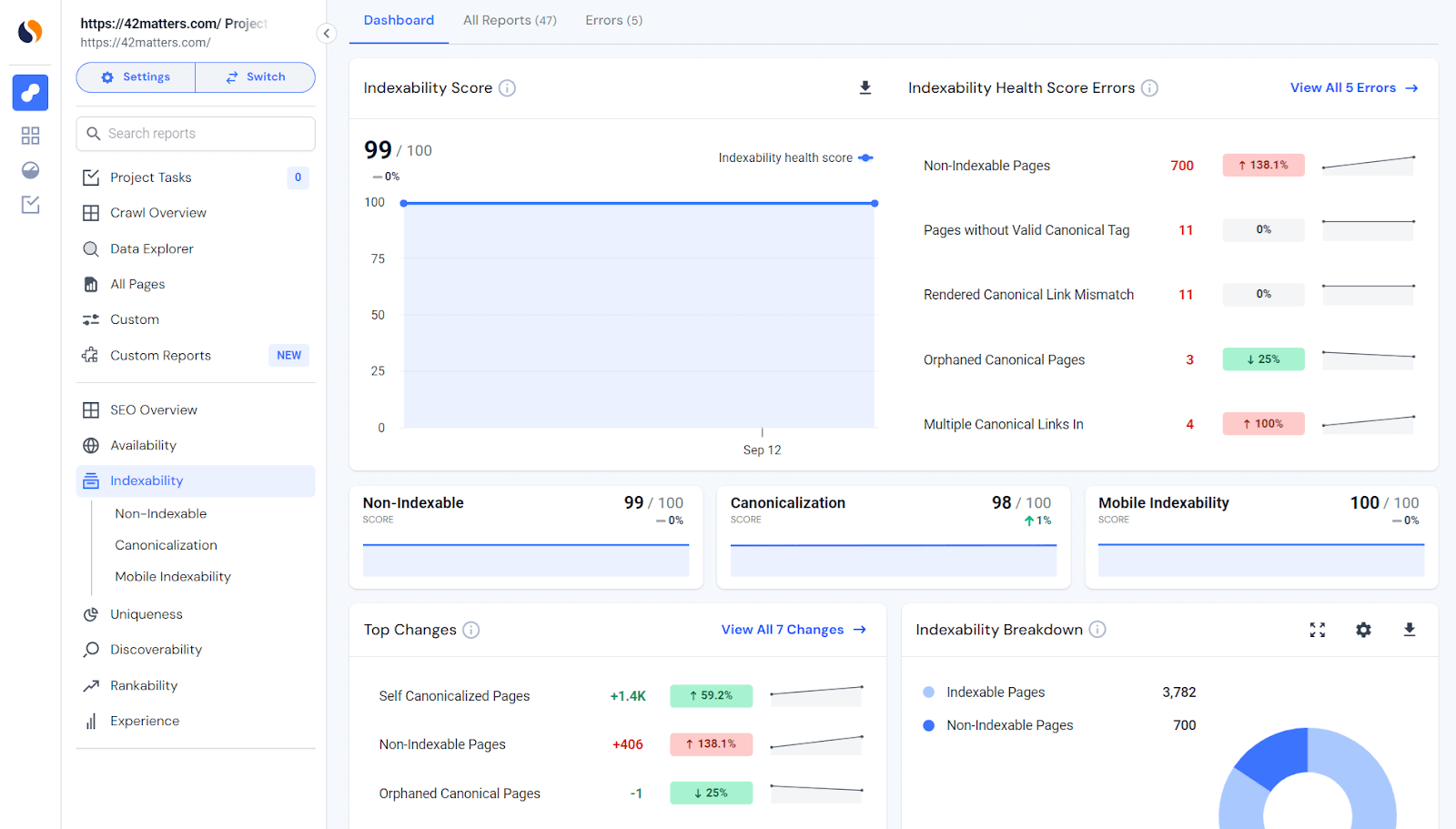
While tools like site: searches and Google Search Console offer valuable insights, they may not reveal the complete picture of indexable URLs or patterns. This is where the Similarweb Site Audits tool excels. It provides in-depth analysis of URLs identified during a crawl.
Start by opening the Site Audit Tool and selecting the “Indexability” option. Examine the Indexability Health Score Errors to uncover anomalies and irregularities.
For instance, a partial crawl might reveal 700 non-indexable URLs compared to 3,782 indexable ones. This mismatch, especially if exacerbated by a complete crawl, could signal crawl budget wastage or crawler traps. If faceted navigation contributes to index bloat, the audit will show a large number of indexable URLs tied to facets. Reviewing the non-indexable report can confirm whether faceted navigation is the culprit—for example, if most URLs in the table are generated by facets. Such patterns strongly suggest a navigation issue that needs resolution.
Fix faceted navigation issues
Resolving faceted navigation issues requires strategic configuration changes that ensure only essential pages are available and visible to search engines. This approach maintains a clean navigational structure while preserving user-friendly navigation.
1. Use canonical tags
Canonical tags inform search engines of the preferred version of a page, consolidating indexing signals and avoiding duplicate content issues. When applied correctly, canonical tags centralize authority on primary pages, improving their ranking potential. This is especially critical in faceted navigation, where duplicate URLs can arise from filter combinations.
2. Leverage robots.txt
The robots.txt file directs search engines to ignore specific pages during a crawl, helping to conserve crawl budget and focus on high-value content. This strategy is particularly effective for addressing crawler traps and ensuring that search engines prioritize the most relevant pages within faceted navigation.
3. Apply nofollow and internal links
Using the nofollow attribute on certain internal links allows you to control which pages search engines index. This strategy redirects search engine attention away from low-priority pages and toward key pages. By leveraging internal links strategically, you can channel authority to significant sections, ensuring that search engines focus on content that matters most for SEO.
4. Implement noindex tags
The noindex tags tag prevents less valuable pages from appearing in search results. When used thoughtfully, these tags ensure that low-priority pages remain hidden without disrupting critical navigational paths. This method is essential for maintaining an organized site architecture and avoiding search index congestion. Proper implementation of noindex tags helps keep your SEO campaign efficient and your site optimized for both users and search engines.
Keep your navigation from cluttering search results while enhancing the user experience
When implemented effectively, faceted navigation can significantly enhance the user experience and boost search engine rankings. Striking the right balance between usability and SEO efficiency can be challenging, but it’s an effort that pays off. By applying targeted SEO strategies, you can unlock the full potential of faceted navigation while keeping your site optimized.
Tools like the Similarweb Site Audit can help identify issues such as index bloat and other navigation-related challenges. Use these insights to refine your website’s SEO and ensure your site stands out in a competitive marketplace.
FAQs
What common mistakes should be avoided in faceted navigation?
Be wary of indexing all the possible faceted combinations on the fly to avoid index bloat and duplicate content issues. Use an informed indexation policy to handle SEO effectively.
Can faceted navigation work well with all ecommerce platforms?
The majority of platforms can use faceted navigation, but each needs a different set of implementations. This depends on how complex and product types your platform catalog contains.
How can I determine which facets need indexing?
Data analysis and user behavior studies can help determine which aspects matter from search patterns and user intent, thus giving guidance to effective indexation choices.
What role do canonical tags play in faceted navigation?
Canonical tags tell search engines which URL is preferred among the duplicate ones, as to help keep PageRank and SEO efficiency consistent without redundant indexing.
Is customer feedback useful for faceted navigation optimization?
Yes, user feedback can help us see the way that customers sort through product options and offerings and fine-tune and maximize faceted filters in congruent with better user needs.
Track Gen-AI And Organic KPI's On The #1 SEO Platform
Give it a try or talk to our marketing team - it’s free!